1. Build Model
-
已有数据,构建模型来使用蓝点预测绿点;
# create Linear Regression Model Class
# almost everything in PyTorch nn.Module (think of this as neural network lego block)
class LinearRegressionModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# 1:start with random weight(this will get adjusted as model learn)
# dtype=torch.float:PyTorch love float32 by default
# requires_grad=True:can we update this value with gradient descent?
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1,dtype=torch.float),requires_grad=True)
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1,dtype=torch.float),requires_grad=True)
# forward define computation in model
# x:input data,e.g. training/testing feature
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
# linear regression formula (y = m*x + b)
return self.weight * x + self.bias2. Model Building Essential
-
Pytorch有四个(give或take)基本模块,可用来创建几乎任何类型的神经网络;
-
它们是 torch.nn,torch.optim,torch.utils.data.Dataset
和 torch.utils.data.DataLoader;
| Module | Memo |
|---|---|
torch.nn |
|
torch.nn.Parameter |
|
torch.nn.Module |
|
torch.optim |
|
def forward() |
|
| Module | Memo |
|---|---|
nn.Module |
contain larger building block(layer) |
nn.Parameter |
contain smaller parameter like weight and |
forward() |
tell larger block how to make calculation on |
torch.optim |
contain optimization method on how to improve parameter |
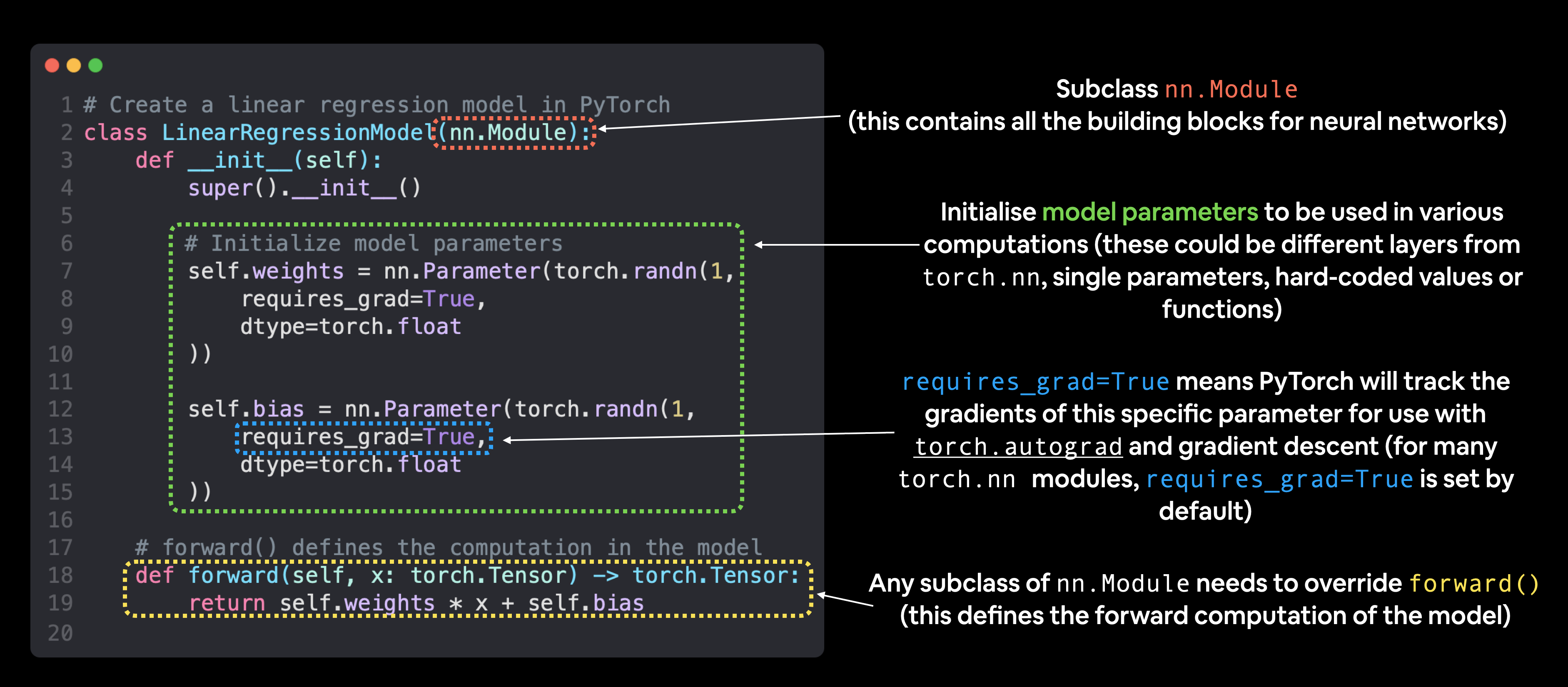
-
通过对nn.Module子类化subclassing来创建Pytorch模型的基本构建块,
对nn.Module的子类对象,必须定义forward()方法;
3. Checking Model Content
-
用创建的类来创建模型实例,并使用 parameters() 检查参数;
-
使用 state_dict() 获取模型的状态(模型包含的内容);
import torch
from torch import nn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# set manual seed since nn.Parameter are randomly initialzied
torch.manual_seed(42)
# create model instance(nn.Module subclass that contains nn.Parameter)
model_0 = LinearRegressionModel()
# check nn.Parameter within nn.Module subclass we create
print(list(model_0.parameters()))
# list named parameter
print(model_0.state_dict())[Parameter containing:
tensor([0.3367], requires_grad=True),
Parameter containing:
tensor([0.1288], requires_grad=True)]
OrderedDict({'weight': tensor([0.3367]), 'bias': tensor([0.1288])})4. Making Prediction
-
making prediction via torch.inference_mode();
-
将测试数据X_test传递给它,看它对y_test的预测有多接近;
# Make predictions with model
with torch.inference_mode():
y_pred = model_0(X_test)
# Note: in older PyTorch code you might also see torch.no_grad()
#with torch.no_grad():
# y_preds = model_0(X_test)
# check prediction
print(f"Testing Sample Number: {len(X_test)}")
print(f"Number of Prediction Made Number: {len(y_pred)}")
print(f"Predicted Value:\n{y_pred}")
plot_prediction(prediction=y_pred)
plt.savefig("VisualizeBuildModelPrediction.svg")
print(f"y_test - y_pred:\n{y_test - y_pred}")Testing Sample Number: 10
Number of Prediction Made Number: 10
Predicted Value:
tensor([[0.3982],
[0.4049],
[0.4116],
[0.4184],
[0.4251],
[0.4318],
[0.4386],
[0.4453],
[0.4520],
[0.4588]])
y_test - y_pred:
tensor([[0.4618],
[0.4691],
[0.4764],
[0.4836],
[0.4909],
[0.4982],
[0.5054],
[0.5127],
[0.5200],
[0.5272]])-
用 torch.inference_mode() 作为上下文管理器进行预测,
这就是 with torch.inference_mode(): 的作用; -
当用模型进行推理/预测时,会使用 torch.inference_mode();
-
torch.inference_mode() 关闭turn off一系列功能,
如梯度跟踪gradient tracking,这是训练所必需,但不是推理所必需,
以使前向传播forward-pass,数据通过forward()更快; -
注:较旧的Pytorch代码中,可能还会看到 torch.no_grad() 用于推理,
torch.inference_mode() 和 torch.no_grad() 类似,
但 torch.inference_mode() 更新,更快,更受欢迎; -
注:每个测试样本有一个预测值,因我们使用的数据类型,对应的直线,一个X值映射到一个y值;
-
ML模型很灵活,可将100个X值映射到一个、两个、三个或10个y值,取决于我们在做什么;